A recent study has unveiled a crucial link between bile acid imbalance and liver cancer, highlighting its role in triggering liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common type of liver cancer. Conducted by a team at the Harvard School of Dental Medicine, this research sheds light on the critical importance of bile acid metabolism in maintaining liver health. By identifying a key molecular switch regulating bile acids, the study opens new avenues for targeted liver disease treatment. Moreover, the discoveries regarding the FXR signaling pathway could revolutionize liver cancer research by providing insights into how to mitigate the harmful effects of bile acid accumulation. As the scientific community continues to unravel these connections, the potential for developing effective therapies becomes increasingly promising.
Exploring the intricate relationship between bile acids and liver health reveals significant implications for understanding hepatic malignancies. This connection between disrupted bile composition and liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, underscores the importance of bile’s role not just in digestion but also in metabolic regulation. The advancements in liver disease treatment outcomes are becoming increasingly vibrant through ongoing liver cancer research, particularly with insights into regulatory mechanisms involving the FXR signaling pathway. Such multi-faceted approaches enable researchers to uncover new strategies to tackle liver ailments effectively. As we broaden our vocabulary around bile dynamics and liver oncology, it becomes evident that addressing bile acid homeostasis is paramount to mitigating cancer risk.
Understanding Bile Acid Imbalance and Its Role in Liver Cancer
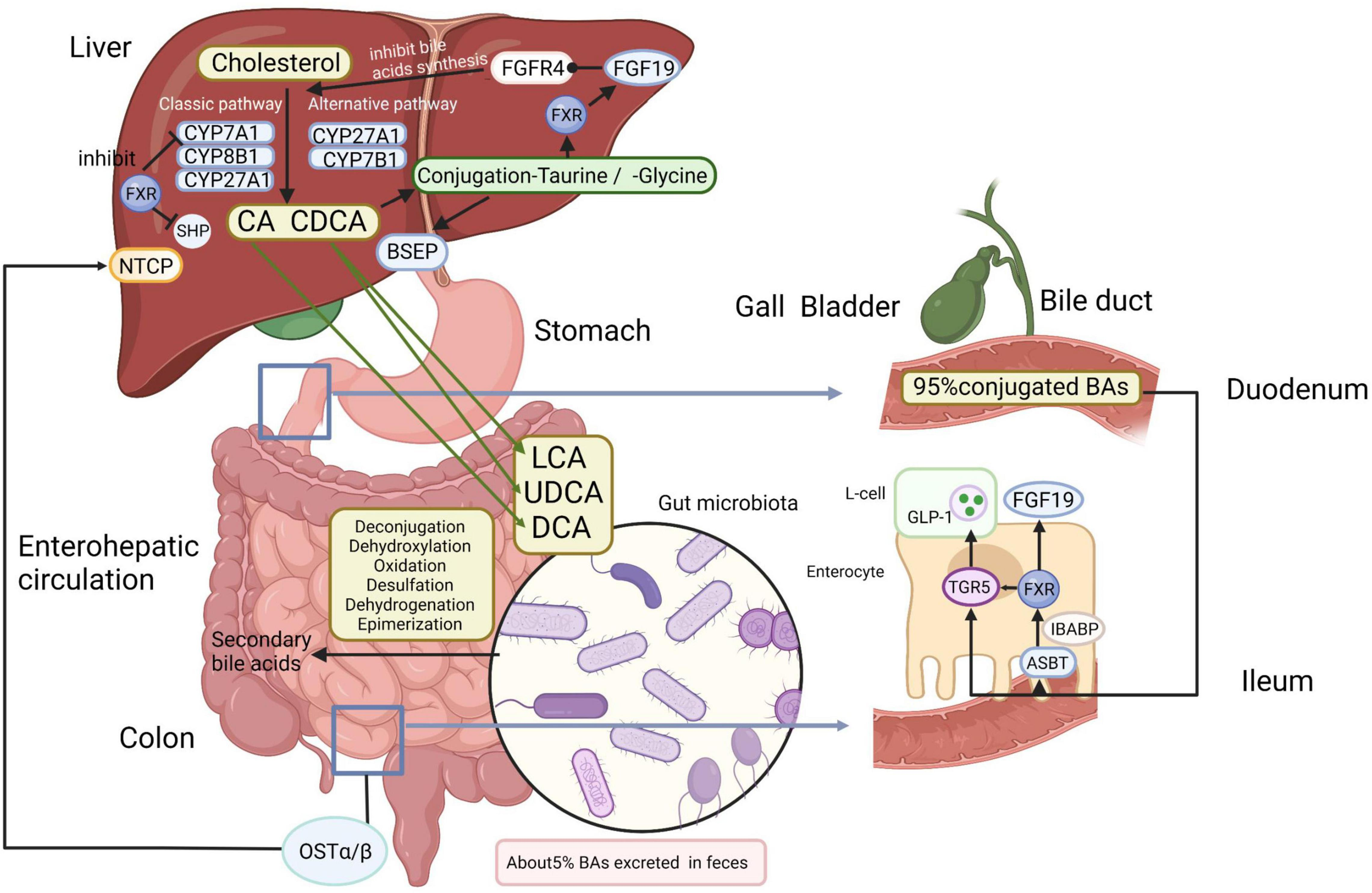
Bile acid imbalance is increasingly recognized as a significant contributor to liver cancer, especially hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Bile acids are not only crucial for fat digestion, but they also influence various metabolic pathways governing liver function. When the delicate balance of bile acid metabolism is disrupted, it can lead to liver injury and inflammation, paving the way for hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent studies have highlighted that abnormalities in bile acid levels can inhibit normal liver signaling pathways, leading to the development of severe liver diseases.
Researchers have pinpointed the role of specific molecular switches, such as the FXR (Farnesoid X receptor), that play a pivotal role in maintaining bile acid homeostasis. An imbalance where bile acids accumulate in the liver can trigger toxic effects through chronic inflammation and fibrosis, further exacerbating the conditions that favor tumor growth in liver tissues. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial in developing effective liver disease treatments aimed at correcting bile acid metabolism.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the connection between bile acid imbalance and liver cancer?
Bile acid imbalance is closely linked to liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Disruption in bile acid metabolism can lead to liver injury and inflammation, which are key contributing factors to the development of HCC. A study has revealed that when bile acids are overproduced, it results in fibrosis and inflammation that can progress to liver cancer.
How does bile acid metabolism affect liver disease treatment?
Understanding bile acid metabolism plays a crucial role in liver disease treatment, especially concerning hepatocellular carcinoma. By regulating bile acids—like enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion—new therapeutic strategies can be developed that may help mitigate liver damage and reduce cancer progression.
What is the FXR signaling pathway and its role in liver cancer?
The FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) signaling pathway is vital for maintaining bile acid homeostasis in the liver. Disruption of FXR function, often due to the activation of YAP, can lead to an overproduction of bile acids. This imbalance contributes to liver inflammation and ultimately the development of liver cancer, highlighting FXR as a potential target for treatment.
Can YAP modulation influence bile acid imbalance and liver cancer risk?
Yes, modulation of YAP can significantly impact bile acid imbalance and reduce liver cancer risk. YAP has been identified as a repressor of FXR, and its activation leads to excessive bile acid accumulation, promoting liver disease. Targeting YAP could restore FXR function and ameliorate the harmful effects of bile acid imbalance.
What are the implications of bile acid imbalance for hepatocellular carcinoma research?
Bile acid imbalance has major implications for hepatocellular carcinoma research by revealing potential molecular targets for intervention. Studies focusing on bile acid regulation, such as FXR and YAP, could pave the way for novel therapeutic strategies in treating liver cancer and advancing liver disease treatments.
How do bile acids act as signaling molecules in liver cancer?
Bile acids serve not only as digestive agents but also as signaling molecules that influence various metabolic processes. Dysregulation of bile acid levels impacts liver signaling pathways, such as the FXR pathway, which is critical to preventing liver inflammation and cancer, thus highlighting their role in liver cancer development.
What therapeutic strategies are being developed to target bile acid imbalance in liver cancer?
Therapeutic strategies targeting bile acid imbalance in liver cancer are focusing on enhancing FXR function and promoting bile acid excretion. Research suggests that activating FXR and inhibiting YAP’s repressive role may offer new pharmacological approaches to reduce liver damage and inhibit HCC progression.
What role does inflammation play in liver cancer development due to bile acid imbalance?
Inflammation plays a pivotal role in the development of liver cancer from bile acid imbalance. When bile acids are overproduced, it leads to liver injury and inflammatory responses, which can contribute to the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma, highlighting the need to manage bile acid levels to prevent such conditions.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Acid Imbalance | A critical imbalance in bile acids can trigger liver diseases, especially hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This has been linked to liver function and metabolism. |
| Molecular Mechanism | A key molecular switch, YAP, regulates bile acid metabolism by repressing FXR, causing bile acid accumulation that leads to fibrosis and inflammation. |
| Research Findings | The study published in Nature Communications presents new insights into potential treatments for liver cancer by focusing on FXR activation and bile acid excretion. |
| Implications | Understanding the role of YAP in metabolic control could lead to new pharmacological solutions for liver cancer. |
Summary
Bile acid imbalance plays a significant role in the development of liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma. This relationship underscores the importance of understanding bile acid regulation in liver health. New research has identified a molecular switch that alters bile acid metabolism, subsequently contributing to liver disease progression. By targeting this mechanism, there is hope for the development of effective treatments for liver cancer that address bile acid imbalance directly.
Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.