**Is sugar addictive?** This question has sparked intense debate among researchers and nutritionists alike. While substances like alcohol and nicotine are classified as addictive based on strict clinical criteria, the effects of sugar on the brain and behavior can mimic addiction-like symptoms. Sugar addiction can drive intense cravings, contributing to a cycle of compulsive eating and heightened desires for sweet foods. Understanding the nutritional impacts of sugar and adhering to sugar intake recommendations is essential in managing its consumption and promoting overall health.
The inquiry into whether sweeteners are habit-forming raises several compelling points about dietary habits and health. Some experts suggest that the psychological and physiological responses our bodies have to sugary foods can lead to patterns similar to those seen in substance dependencies. Terms like “sugar cravings” and the long-term effects of excessive sugar consumption indicate a need for awareness about these cravings and their potential ties to unhealthy eating practices. As we delve deeper into the conversation about sugar and sweet textures, it’s crucial to distinguish between moderate enjoyment and overindulgence, ensuring we maintain a balanced diet.
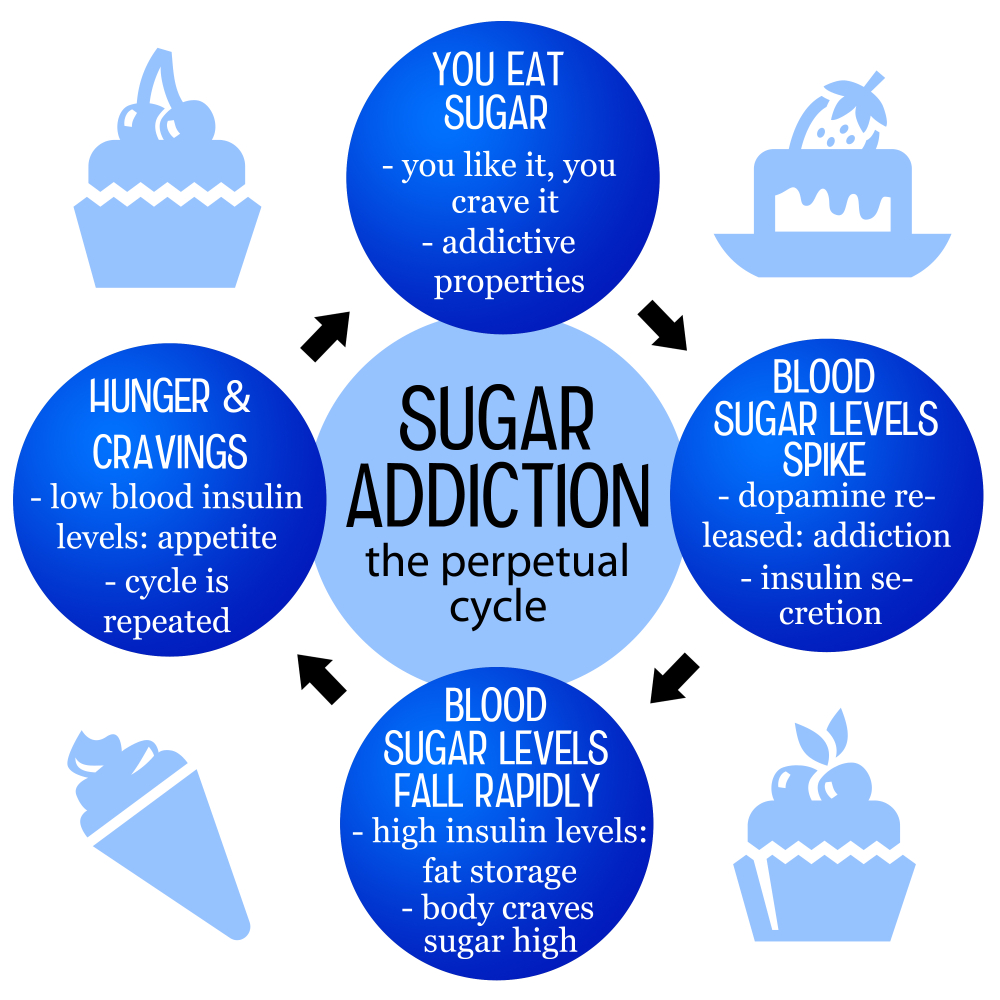
Understanding Sugar Addiction
The concept of sugar addiction raises numerous debates among nutrition experts and researchers. While substances like alcohol and nicotine are classified as addictive due to their psychological and physical dependence, sugar is a bit more complex. Although scientific studies have shown that sugar can activate the brain’s reward pathways, leading to increased cravings and potentially compulsive eating behaviors, it is essential to understand that sugar isn’t treated the same way as other addictive substances. Its presence in our daily diet in moderate amounts can be significantly beneficial, which complicates the narrative surrounding sugar addiction.
Yet, the increasing consumption of added sugars, particularly from processed foods, can lead to adverse health effects. Regular intake of these high-sugar foods can diminish self-control and heighten cravings, creating a cycle of dependence that many individuals struggle to break. Although not classified as addictive in a clinical sense, the withdrawal-like symptoms experienced when reducing sugar intake—such as mood swings and headaches—can feel very real, highlighting the complex relationship between sugar and cravings.
The Effects of Sugar on Health
Consuming high amounts of sugar can have profound effects on overall health. Research consistently points to the correlation between excessive sugar intake and various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. The average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, far exceeding the American Heart Association’s recommendation of no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 for women. This excess can lead to significant health problems, underscoring the importance of understanding sugar’s impact on nutrition.
Additionally, sugar affects metabolic health and can alter hunger hormones, leading to increased appetite and weight gain. The consumption of sugar-rich foods, especially ultra-processed options, can disrupt the balance of nutrients in the diet, often displacing healthier choices. Thus, it’s crucial to recognize the detrimental effects associated with high sugar consumption and to adopt healthier eating habits that include lower sugar options, fulfilling dietary recommendations, and maintaining proper nutrition for better health outcomes.
Nutritional Impacts of Sugar on Your Diet
Sugar can significantly affect the nutritional balance within our diets. While sugars found in natural sources like fruits and vegetables provide essential nutrients, added sugars found in processed foods contribute little to overall nutrition. When people consume large quantities of added sugars, they often do so at the expense of more nutrient-dense foods, leading to deficiencies in critical vitamins and minerals. This imbalance can create a reliance on sugar-laden snacks that offer little to no nutritional value.
Incorporating moderation into sugar intake is essential for maintaining a well-rounded diet. Understanding how much sugar is in your food and choosing whole foods with lower added sugar content can help improve dietary quality. By prioritizing healthy food choices and reducing reliance on sugary products, individuals can minimize the negative nutritional impacts of sugar and enhance their overall well-being.
Sugar Intake Recommendations for a Healthy Lifestyle
Following sugar intake recommendations is vital for fostering a healthy lifestyle. Organizations such as the American Heart Association provide explicit guidelines on sugar consumption, emphasizing that moderation is key. Keeping your intake within the recommended limits helps to avoid the health risks associated with high sugar diets, such as obesity and metabolic syndrome. By being mindful of the sugar content in foods and beverages, one can strategically improve their health while making satisfying dietary choices.
Moreover, it is beneficial to recognize that not all sugars are created equal. Natural sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provide a wealth of nutrients and fiber, promoting satiety and overall health. Conversely, added sugars, generally found in sweets and processed foods, should be minimized. Adhering to recommended daily sugar intake can lead to significant health benefits, allowing for a balanced diet that includes a variety of foods, enhancing one’s physical well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar can trigger cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance by clinical standards like alcohol and nicotine. However, the effects of sugar on the brain and behavior can lead to heightened cravings and a reliance on sweet foods, making it difficult for some individuals to cut back on sugar consumption.
What are the effects of sugar on the brain that may suggest sugar addiction?
Sugar has been shown to affect brain chemistry, increasing dopamine release similarly to addictive substances. This can lead to strong cravings and habitual consumption, as the brain learns to associate sugar with pleasure and reward, resulting in withdrawal-like symptoms when intake is abruptly decreased.
How does sugar intake affect cravings and eating behaviors?
High sugar intake can lead to increased cravings for sweet foods due to its palatability and addictive-like qualities. People often find themselves reaching for more sugary snacks and beverages, creating a cycle of craving and consumption that can be difficult to break.
What are the nutritional impacts of excessive sugar consumption?
Excessive sugar intake can lead to various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to no more than 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women to maintain better health and reduce the risk of these conditions.
What are the recommended limits for sugar intake to avoid sugar addiction?
To prevent potential sugar addiction and its negative health effects, the American Heart Association advises that men should limit added sugar intake to 9 teaspoons per day and women to 6 teaspoons. Children should consume even less, emphasizing the importance of monitoring sugar consumption through reading food labels.
Can reducing sugar intake cause withdrawal symptoms similar to addiction?
Yes, when individuals significantly reduce their sugar intake, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches, anxiety, and mood swings. This is due to the brain’s dependency on sugar for immediate energy and pleasure, which can create a cycle of cravings.
Is some sugar essential for a balanced diet?
Yes, some sugar is necessary for a balanced diet, as it occurs naturally in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. The key is to consume it in moderation and focus on whole foods rather than processed sugars found in sweets and sugary drinks.
How can I reduce my sugar intake without feeling deprived?
To successfully reduce sugar intake, it’s best to do so gradually instead of going cold turkey. Incorporate more whole foods into your diet, such as fruits and vegetables, and read food labels to better understand sugar content. This approach helps satisfy cravings while decreasing overall sugar consumption.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Addictive Qualities | Sugar has been shown to cause cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, leading some to consider its addictive nature. |
| Not Classed as Addictive | Unlike alcohol, nicotine, and drugs, sugar is not classified as an addictive substance by clinical criteria. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Stopping sugar consumption can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety, but these are less severe than those associated with drugs. |
| Dietary Need | Sugar is present in many necessary foods (fruits, grains, dairy) that are essential for survival, unlike substances that can be completely eliminated. |
| Moderation is Key | Low to moderate sugar consumption won’t cause serious health effects; awareness of added sugar intake is important. |
| Gradual Reduction Recommended | Suddenly eliminating sugar can be counterproductive; reducing intake gradually is advised. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? The debate continues, but current research suggests that while sugar may have addictive qualities, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. Sugar does trigger cravings and can lead to habitual consumption, particularly when found in ultra-processed foods. However, it is crucial to distinguish between the role of sugar as a dietary need and the harmful effects of substances that are truly addictive. Consuming sugar in moderation is perfectly healthy, and being aware of added sugar intake is vital for maintaining a balanced diet. Therefore, we should focus on reducing sugar gradually rather than eliminating it completely, to enjoy its benefits without overindulging.
Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.