Bile imbalance liver cancer is an emerging focus within the realm of liver disease research, highlighting the intricate relationship between bile acids and cancer progression. Recent studies have uncovered how abnormalities in bile acid production can lead to severe liver conditions, most notably hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the prevalent type of liver cancer. By identifying the critical molecular switch affecting bile acid regulation, researchers are paving the way for innovative liver cancer treatments. The findings suggest that targeting the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway may unlock new therapeutic avenues by correcting the bile imbalance. With this understanding, ongoing liver disease research strives to develop effective strategies to combat liver cancer and improve patient outcomes.
The connection between bile acid irregularities and liver malignancies offers a fresh perspective in the fight against liver diseases. Terms like bile acid dysregulation, hepatic tumorigenesis, and hepatocellular malignancies are crucial for understanding how fluctuations in bile components can initiate a cascade of detrimental biological events. With the critical role that bile acids play—not only in digestion but also in cellular signaling—it becomes increasingly vital to investigate their influence on liver health. Recent advancements in the field of liver disease research have shed light on the potential of targeting specific molecular pathways, particularly those involving YAP FXR signaling, to mitigate the risks of liver cancers. As scientists delve deeper into these complex interactions, hope arises for developing new and effective liver cancer treatment options.
Understanding the Role of Bile Acids in Liver Cancer
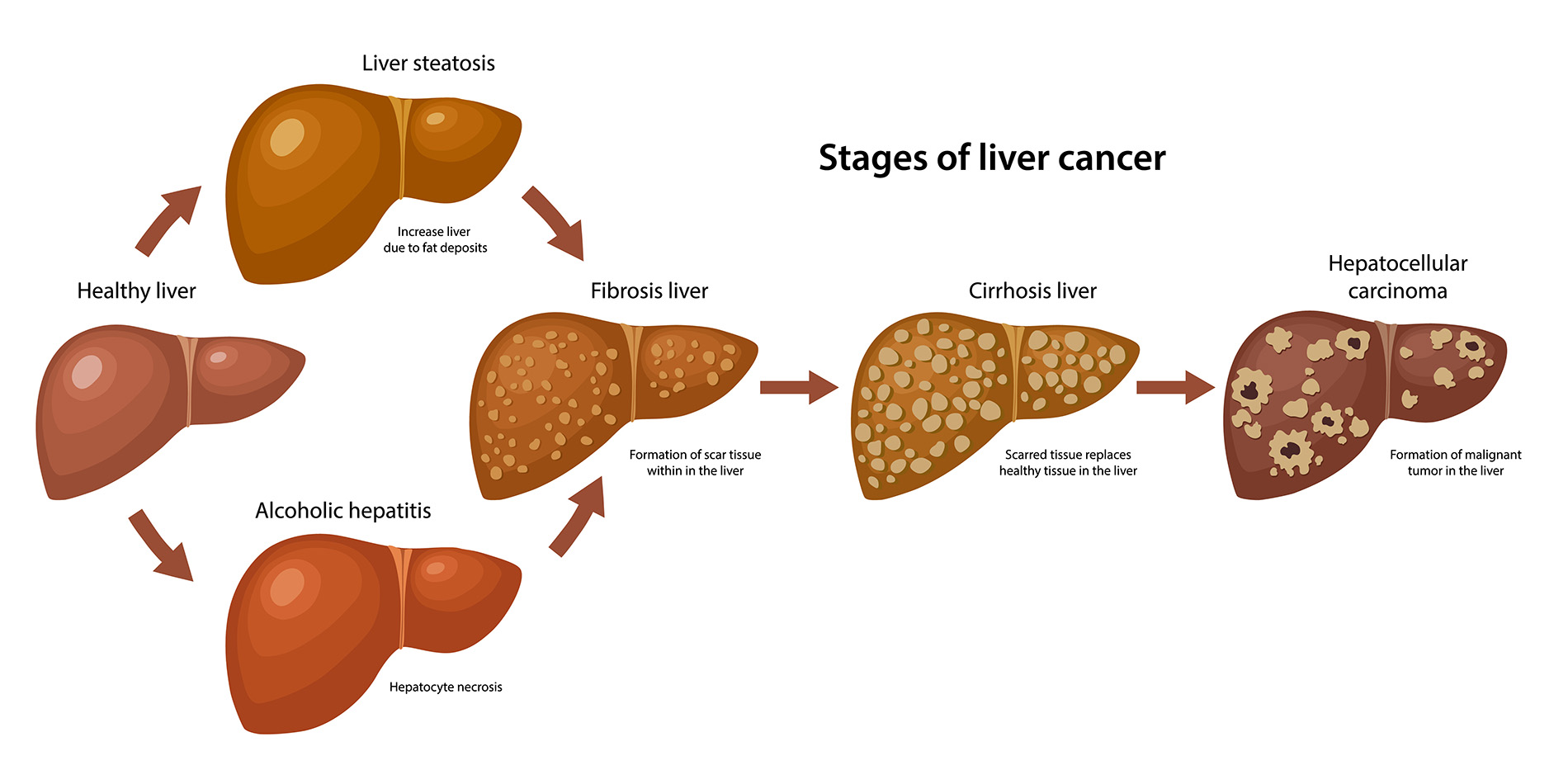
Bile acids are not only essential for the digestion and absorption of fats but also play a pivotal role in maintaining metabolic homeostasis. Recent studies have illustrated a significant connection between bile acid imbalances and liver cancer, specifically hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). When the production and excretion of bile acids are disrupted, it triggers a cascade of damaging processes within the liver. This imbalance can lead to liver inflammation and fibrosis, which are well-known precursors to the development of liver cancer.
In the context of liver cancer treatment, understanding these mechanisms has led to new therapeutic targets. For example, the study conducted by Yingzi Yang highlights the molecular switch that regulates bile metabolism, revealing how the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway can influence bile acid levels. By targeting this pathway, researchers hope to restore normal bile acid homeostasis, potentially offering new avenues for effective treatments against liver cancer.
The Significance of YAP FXR Signaling in Liver Disease
The YAP (Yes-associated protein) and FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) signaling pathways are crucial in managing bile acid metabolism within the liver. Research has shown that the activation of YAP can inhibit the function of FXR, provoking an environment where excessive bile acids accumulate. This accumulation not only contributes to liver injury but also enhances the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma. As a central player in liver disease, understanding the dynamics of YAP and FXR could be the key to unlocking new treatment strategies for liver cancer.
Recent findings suggest that pharmacologically activating FXR or inhibiting YAP could reverse the detrimental effects of bile acid overproduction. By promoting bile acid excretion and improving liver function, these interventions may protect against liver diseases and significantly reduce the risk of liver cancer progression. Ongoing research will be essential to explore these therapeutic options further, with the goal of not only treating but also preventing liver cancer through better management of bile metabolism.
Implications of Bile Imbalance for Liver Disease Research
The implications of bile imbalance extend far beyond liver cancer treatment; they highlight the necessity for ongoing liver disease research to uncover how metabolic processes contribute to various hepatic conditions. As researchers like Yingzi Yang delve into the mechanisms behind bile acid regulation, it becomes increasingly clear that the liver’s complex signaling pathways must be understood in greater depth. Such research efforts are critical, as they can uncover new biomarkers for liver disease and pave the way for novel therapeutic approaches.
Additionally, exploring the correlation between bile acids and liver health may lead to advancements in personalized medicine for patients at risk of liver cancer. By identifying those with bile metabolism disorders, healthcare providers can implement preventive strategies tailored to individual metabolic profiles. Such personalized interventions could drastically reduce the incidences of liver disease and improve overall patient outcomes, showcasing the vital role of ongoing liver disease research.
The Future of Liver Cancer Treatment Strategies
As new insights into bile metabolism and its link to liver cancer emerge, the future of treatment strategies appears bright. Current research indicates that manipulating the YAP-FXR pathway presents an exciting opportunity to address not only hepatocellular carcinoma but other related liver diseases as well. Therapies aimed at enhancing FXR function or inhibiting YAP’s repressive network could mark a significant shift in how liver cancer is approached.
Moreover, as the understanding of bile acids expands, it is likely that new classes of drugs will be developed specifically targeting these pathways. This blossoming field of liver disease research is poised for breakthroughs, especially as collaborations between institutions and pharmaceutical companies grow. The hopeful prospect of introducing innovative therapies—rooted in molecular understanding—underscores the importance of continued investment in liver disease research and treatment development.
Impact of Lifestyle on Bile Acid Regulation
Lifestyle factors play a critical role in the regulation of bile acids and, consequently, liver health. Diet, physical activity, and overall metabolic health influence bile production and metabolism. An imbalance in these factors can exacerbate the risk of liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Studies suggest that adopting a healthier diet rich in fiber and low in saturated fats can promote better bile acid balance and improve liver function, potentially decreasing the likelihood of liver cancer.
Additionally, regular exercise has been shown to improve metabolic health, thereby positively affecting bile acid dynamics. With the mounting evidence linking lifestyle changes to improved bile metabolism, public health initiatives aimed at promoting healthier behaviors could serve as a frontline defense against liver diseases. Further exploration into the relationship between lifestyle and liver cancer prevention could empower individuals to take actionable steps towards better health.
Exploring the Genetic Factors of Liver Cancer
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the development of liver cancer, particularly in individuals with bile acid metabolism disorders. The genetic makeup can influence how individuals process bile acids and manage liver function. Studies are increasingly focusing on the identification of specific genetic markers that predispose certain populations to hepatocellular carcinoma, emphasizing the need for personalized approaches in liver disease management.
By unraveling the genetic factors associated with liver cancer, researchers can develop more targeted treatment protocols that consider individual genetic backgrounds. This innovative approach could lead to the design of tailored therapies, optimizing efficacy while minimizing side effects in liver cancer patients. As research progresses, understanding these genetic linkages will be pivotal in providing life-saving treatments for those facing liver disease.
The Role of Biomarkers in Liver Cancer Diagnosis
Biomarkers hold immense potential in diagnosing liver cancer, especially in patients with bile acid metabolism disorders. Identifying specific biomarkers associated with bile acid imbalances can facilitate earlier detection of hepatocellular carcinoma and improve prognosis. The current research emphasizes the importance of developing non-invasive tests that can screen for these biomarkers, potentially enabling timely interventions for at-risk populations.
With advances in genomic and proteomic technologies, researchers are making strides in discovering new biomarkers that correlate with liver cancer progression. This shift not only enhances the diagnostic landscape but also opens doors for personalized treatment strategies targeting the specific molecular signatures found in an individual’s liver disease profile. Continued exploration of biomarkers will undoubtedly reshape how liver cancer is diagnosed and treated in the future.
Advancing Pharmacological Solutions for Bile Disorders
The potential for pharmacological interventions to correct bile acid imbalances is a burgeoning area of research that could transform liver cancer treatment. By targeting the underlying mechanisms outlined in recent studies, pharmaceutical companies are developing drugs aimed at restoring bile acid homeostasis. These treatments are especially relevant for those with metabolic syndromes that predispose them to liver diseases, highlighting the need for collaborative efforts between researchers and drug developers.
As these pharmacological solutions reach clinical trials, their efficacy in preventing or reversing liver damage—and ultimately hepatocellular carcinoma—will be rigorously assessed. This focus on drug design that specifically targets bile acid metabolism could not only mitigate the effects of liver cancer but also revolutionize how liver diseases are managed on a broader scale. The excitement surrounding these potential treatments underscores the importance of ongoing research into the relationship between bile acids and liver health.
Integrating Multidisciplinary Approaches in Liver Disease Research
Integrating multidisciplinary approaches in liver disease research is vital for tackling the complexity of conditions such as hepatocellular carcinoma. By combining insights from molecular biology, genetics, clinical medicine, and lifestyle research, a more holistic understanding of bile acid metabolism and its implications for liver health can be achieved. Collaborative efforts among experts in these fields can lead to innovative strategies that address the multifactorial nature of liver diseases.
Such collaborations can also enhance the development of comprehensive treatment plans that incorporate lifestyle changes, pharmacological interventions, and genetic testing to provide a personalized approach to liver cancer prevention and treatment. By fostering a multidisciplinary environment, researchers can bridge gaps in knowledge and cultivate novel solutions that directly translate into improved patient outcomes in liver disease management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the connection between bile imbalance and liver cancer treatment?
Bile imbalance plays a critical role in liver cancer treatment, particularly in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Disruption in bile acid production can lead to liver injury and inflammation, increasing the risk of cancer. Researchers are exploring therapies that target the regulation of bile acids and the FXR receptor, which could offer new avenues for effective liver cancer treatment.
How do bile acids influence the development of liver cancer?
Bile acids have a dual role in metabolism and can influence the development of liver cancer, notably HCC. An imbalance in bile acids can trigger inflammation and fibrosis, conditions that promote tumor formation. Recent studies reveal that the YAP FXR signaling pathway is pivotal in regulating bile acid homeostasis, and its dysfunction can lead to liver cancer.
What role does YAP FXR signaling play in bile acids and cancer?
YAP FXR signaling is essential in maintaining bile acid balance in the liver. YAP, when activated, can repress FXR function, leading to excessive bile acid accumulation. This disruption is linked to liver disease progression and hepatocellular carcinoma. Understanding this signaling pathway opens potential therapeutic targets for liver cancer treatment.
Can liver disease research reveal new insights into bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Yes, liver disease research is crucial for understanding the links between bile imbalance and liver cancer. Ongoing studies focus on the mechanisms through which bile acids affect liver health and the pathways involved in liver cancer development, like YAP FXR signaling, to identify new treatment strategies.
What improvements might arise from regulating bile acid metabolism in liver cancer patients?
Regulating bile acid metabolism may offer significant improvements in liver cancer patients. By targeting the FXR receptor or inhibiting YAP’s repressive effects, researchers aim to reduce liver damage and cancer progression. Such interventions could enhance treatment outcomes and possibly prevent the onset of hepatocellular carcinoma.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance | Bile imbalance, specifically in bile acids, can trigger liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This imbalance is linked to metabolic processes regulated by bile acids. |
| Molecular Switch Identified | Research identified YAP as a molecular switch that promotes tumor formation by interfering with the bile acid sensor FXR, disrupting bile acid homeostasis. |
| Effects of YAP Activation | YAP activation leads to overproduction of bile acids, liver inflammation, and ultimately liver cancer. |
| Potential Treatment Targets | Blocking YAP’s repressor activity or enhancing FXR function could provide therapeutic strategies to prevent liver damage and cancer progression. |
| Research Implications | The findings are significant for understanding metabolic control in liver biology and cancer, possibly leading to new pharmacological solutions. |
Summary
Bile imbalance liver cancer has emerged as a crucial area of research, highlighting the role of bile acids in liver health and disease. The recent identification of molecular pathways linking bile imbalance to hepatocellular carcinoma underscores the need for further studies and potential therapeutic interventions. Researchers are optimistic that enhancing bile acid regulation could pave the way for innovative treatments, offering hope in the fight against liver cancer.
Comments are closed, but trackbacks and pingbacks are open.